FDM printing and how it differs from MJF
It simply isn’t viable to use casting in small-batch production, so manufacturers resort to additive technologies to save time and money. The build starts as a 3D model, which is loaded into the 3D printer and then printed layer by layer. With this technology, components can be made from virtually any material, e.g., plastic, gypsum, sand, powder, composites, and even metal.
There are dozens of additive processes out there. Here, we will compare only two of them: fused deposition modeling (FDM) and multi-jet fusion (MJF).
FDM technology
FDM or fused deposition modeling is a 3D printing technology that works by depositing molten filament on the platform layer by layer.
Let’s take a closer look.
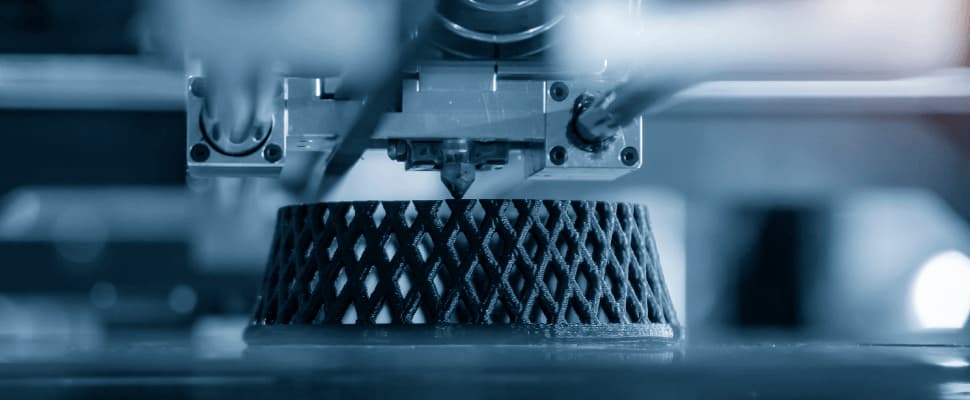
Preparation. Before actually using the 3D printer, you need to make an STL 3D model, which you can do in any 3D modeling software on PC, e.g., SolidWorks, ZBrush, and Autodesk 3DS Max. Once completed, the model is checked for inverted polygons, bad edges, and other defects.
After all the checks are complete, the model is loaded into the slicing software, which calculates the trajectory for layer-building, as well as filament feed rate and temperature. If the model has any overhanging elements, supporting elements are added automatically. At this stage, the model is converted into code that controls the printer’s moving parts.
Printing. FDM uses 1.75 mm and 3 mm filament as feedstock and support material. Usually, the filament comes in cartridges or spools. It’s fed into the extruder’s heater, where it is heated to melting point.
The molten material then exits through the nozzle and onto the moving platform. Throughout the extrusion, the platform moves up and down, while the extruder moves on an XY plane. The moving parts are controlled by the 3D model code from the slicing software.
Once all the layers have been completed, the finished item is then detached from the platform and cleaned up of all the supporting elements and excess polymer.
Advantages of FDM technology
Low cost. FDM is a simple and widely used printing technology. Its biggest advantage is accessibility at low cost. No need to buy an entire 3D printer: many owners upgrade their equipment gradually, assembling it bit by bit. All modules are available for purchase online.
Variety of polymers. There is a wide variety of feedstock materials available for FDM technology: differently colored, transparent, glossy, and matte, as well as more rigid and flexible. You can also choose metalized plastic or wood-filled feedstock. Even fluorescent, luminescent, and water-soluble polymers are available for FDM.

However, not all the materials mentioned would fit an FDM printer. Polymers have different melting temperatures, so it’s the printer nozzle heating temperature that determines what materials can be used. For instance, if the extruder nozzle can’t heat above 150 °C, and the filament melts at 170 °C, the printer will be unable to print the model.
Drawbacks of FDM technology
Imprecision. FDM’s main downside is its low resolution and dimensional precision as compared to other 3D printing technologies. It can’t be used for high-resolution builds and complex geometry.
Fragility. FDM-printed models are anisotropic, meaning that they are not resistant to mechanical loads, and temperature fluctuations increase the risk of lamination.
Finishing. Newly printed items have visible seams between layers and require finishing. Overhanging parts require supporting elements to be printed. After the printing is complete, they have to be removed.
Applications
FDM printing is used in many fields. The technology is widely used in small-batch production, as well as in the production of prototypes and functional components. Architectural and anatomic models, souvenirs, and car tuning parts can all be printed on FDM printers.
However, the quality is inferior to that produced by industrial printers. If you need higher precision, you would be better off using a modern powder printing technology like MJF. So how does MJF work?
How MJF technology works
MJF or Multi Jet Fusion is a powder 3D printing technology. Items are printed using a special polyamide. The powder is applied to the print bed, then a bonding agent is added, and the material is fused with IR light. Then, another layer of polyamide is added, and the process repeats. Let’s look at how the MJF technology works using the HP Jet Fusion 5210 3D printer as an example.
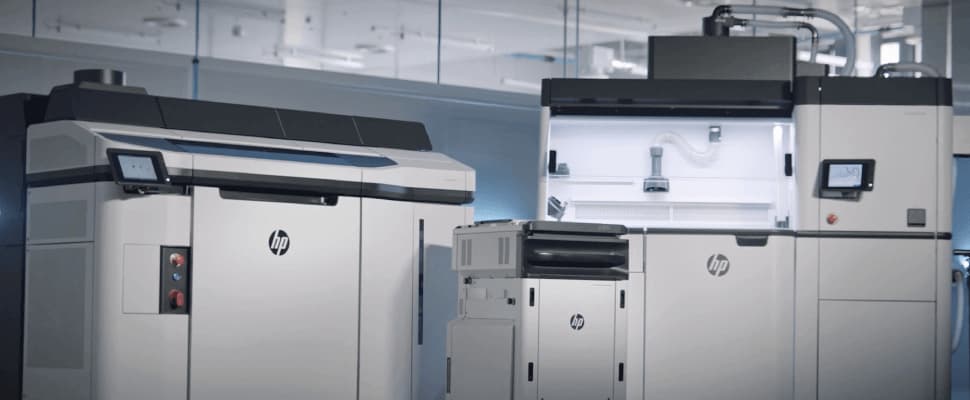

Preparation. The 3D model development process is the same as for the FDM technology. Once the 3D model is finished and loaded into the printer, equipment preparation begins. Before the printing starts, the printer’s reservoir is filled with the PA 12 polyamide powder. Then the reservoir is connected to the printer, and the printer is launched.
Printing. The entire process takes place within the printer chamber, which is 380 × 284 × 380 mm in size. Here, the moving printing head applies the first layer of polyamide onto the base. A bonding agent is applied to match the model’s layer, and an IR lamp passes over its surface. The powder and the agent are thus fused, then another layer of polyamide is added, and the process is repeated.
Cooling. The printed items are then removed from the printer for cooling. For the material to retain its properties, the items are cooled gradually over 4 to 12 hours. Meanwhile, the printer starts building another batch. This makes MJF an excellent choice for uninterrupted manufacturing and large-scale production.
Clean-up. Once the items cool down, the excess powder is removed, and the items in the chamber are cleaned up by sandblasting. The printed items are now complete and can be painted if needed.
Advantages of MJF technology
Resolution. MJF technology produces highly detailed items. Models are printed with a resolution of 1,200 DPI. The minimal layer thickness is close to that of a human hair—only 0.08 mm. Thanks to this, high reproducibility can be achieved regardless of the batch size.

PA 12 is a durable and load-resistant material It’s a high-density thermoplastic. As a result, the MJF-printed items are durable and resistant to moisture and high temperatures. For instance, ABS melts at 105 °C, and PA 12 at 187 °C. The material is resistant to the chemical effects of greasing agents, hydrocarbons, and alkaline mediums. It also retains its properties under UV radiation.
Printing speed. The printer’s IR lamp covers the entire build area. Therefore, all the items inside can be printed simultaneously. This helps ensure outstanding build speed. With FDM, you can print 36 identical items within three hours, whereas the HP MJF can print over 1,000 in the same time.
Savings. MJF technology lets you print items with complex geometry without any support elements. As a result, printing consumes less material, reducing costs. Not only that, but it even allows excess polyamide to be reused.
Drawbacks of MJF technology
Поверхность. Детали, напечатанные с использованием MJF-технологии, имеют шероховатую поверхность. Чтобы ее сгладить, изделие передают на постобработку.
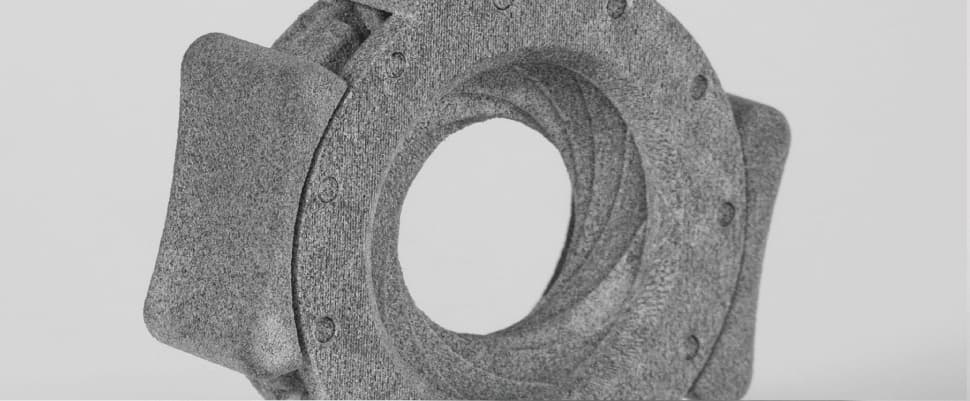
Surface quality. MJF-printed items have a rough surface and need to undergo finishing to smooth it.
MJF technology accessibility
MJF 3D printers are expensive industry-grade equipment. They can cost up to hundreds of thousands of dollars, and people need to undergo special training to use and service them. Furthermore, only the equipment supplier (Hewlett-Packard) can provide that training.
MJF technology accessibility
The Ukrainian company Infomir provides 3D printing services on Eastern Europe’s only HP Jet Fusion 5210 printer. The company accepts orders for prototypes, functional components, prosthetics, anatomic models, and batch item printing.
To find out the price, you need only upload your 3D model into the price calculator. You can also place your printing order on the same page.
FDM and MJF are both affordable 3D printing technologies. They are excellent alternatives to casting when it comes to prototyping and small-batch production. FDM printing is the best choice when you need a budget-friendly solution. However, if you need high-resolution items built fast, you would be better off going with MJF.


