Using thermoplastic polyurethane for MJF 3D printing
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is one of the most popular materials for Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) 3D printing. The unique properties of TPU — flexibility, transparency, and resistance to oil, grease, and abrasion — mean that the material can be used for manufacturing a variety of products: from industrial parts to consumer goods. In this article we’ll explain the features of TPU , its advantages, and practical applications.
What exactly TPU is
TPU is a multipurpose polymer with high elasticity, durability, and resistance to various environmental influences. These characteristics are determined by its segmented structure, combining soft and flexible as well as hard crystalline components. As a result, we have a material that can withstand significant deformation and stress, making it suitable for products that require both flexibility and strength.
MJF technology
MJF is an innovative 3D printing technology developed by Hewlett-Packard. The steps of the printing algorithm are described below.
Material application: a thin layer of powder, such as TPU, is spread over the work platform.
Agent application: detailing and sintering agents are applied to the powder according to the loaded 3D model.
Sintering: infrared lamps run over the layer, fusing the areas with the thermo-fusing agent.
Layering: the process is repeated layer by layer until the part is complete.
Advantages of using TPU in MJF
Flexibility and durability: the inherent flexibility of TPU allows for the creation of parts that can withstand numerous bends and stretches while maintaining the product’s consistency. This is valuable for manufacturing products such as gaskets, seals, and footwear where flexibility is essential.
Chemical resistance: TPU’s resistance to oils, greases, and various chemicals extends the life of parts used in unusual environments. These characteristics are required in the production of automotive parts and industrial equipment.
Wear resistance: the material’s high wear resistance makes it appropriate for parts exposed to frequent friction and mechanical stress, such as conveyor belts and gears.
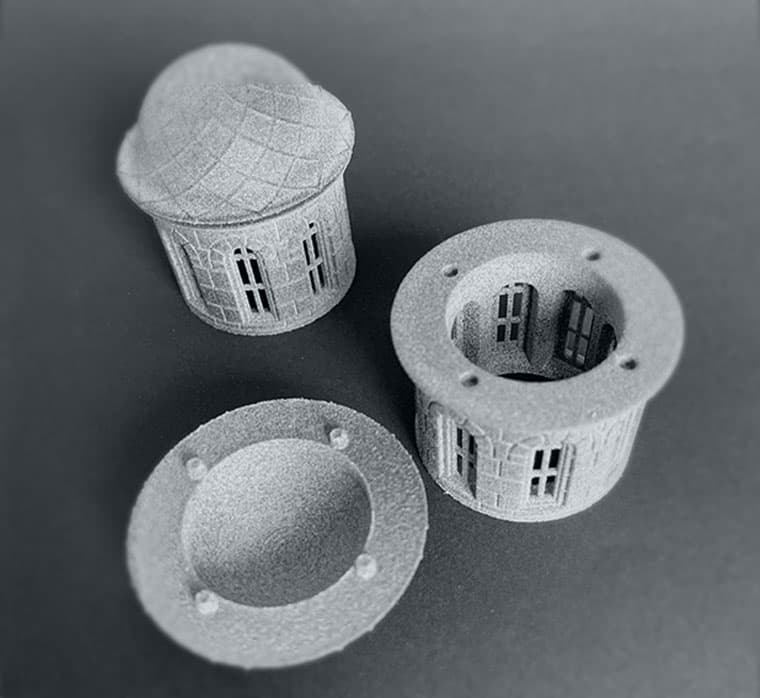
Customization and complexity: the precision of MJF enables the manufacturing of detailed and complex geometric forms. TPU’s adaptability enhances this aspect even further, creating customized and complex designs to meet specific functional requirements.
TPU characteristics
For a clearer understanding of the thermoplastic polyurethane advantages, this table shows the material’s main characteristics:
Practical TPU applications
Footwear: TPU’s flexibility and durability make it an optimal material for manufacturing customized footwear components, including midsole and insole. This is possible due to MJF technology that can create complex constructions, in turn increasing the comfort and performance of the final product.
Medical devices: TPU is used in the production of medical components such as prosthetics and orthotics, where flexibility and patient-specific customization are essential. MJF allows for the production of detailed customized devices that improve fit and functionality.
Automotive parts. TPU’s resistance to oils and greases makes the material ideal for producing seals, gaskets, and other components exposed to harsh environments. MJF’s precision ensures that these parts will meet strict industry standards.
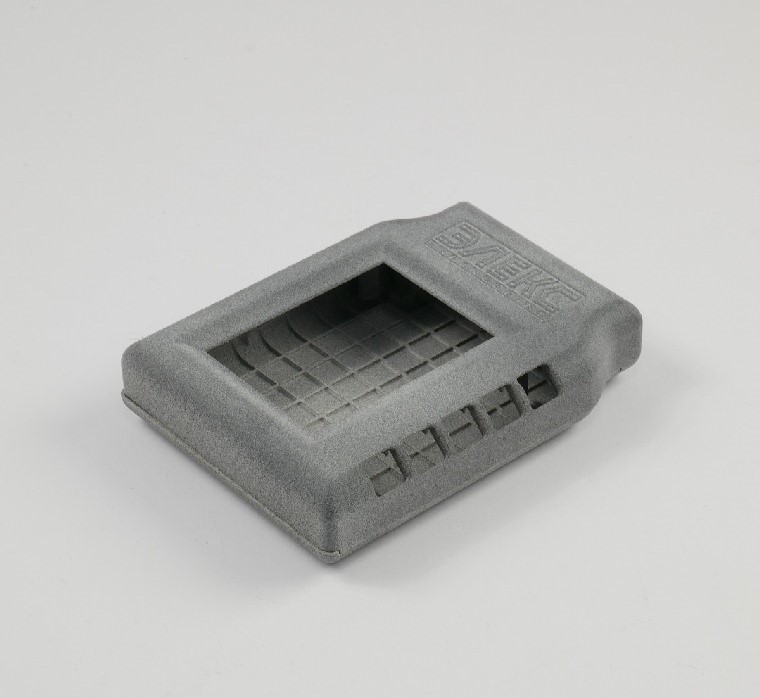
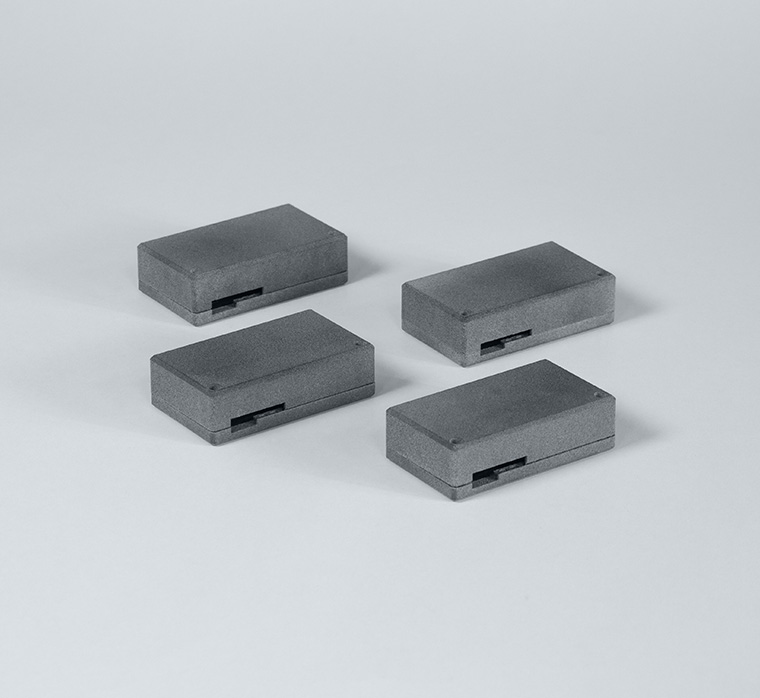
Consumer electronics: due to its durability and flexibility, TPU is used to print protective covers and flexible consumer electronics components. MJF can be used to create durable, customized parts that protect delicate electronics from damage.
Using thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) with Multi Jet Fusion 3D printing offers many opportunities in a variety of industries. TPU material can be used to produce high quality, durable, and complex parts customized for specific purposes. All of this makes it a valuable material in the growing field of additive manufacturing.